Need Full Specifications?
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
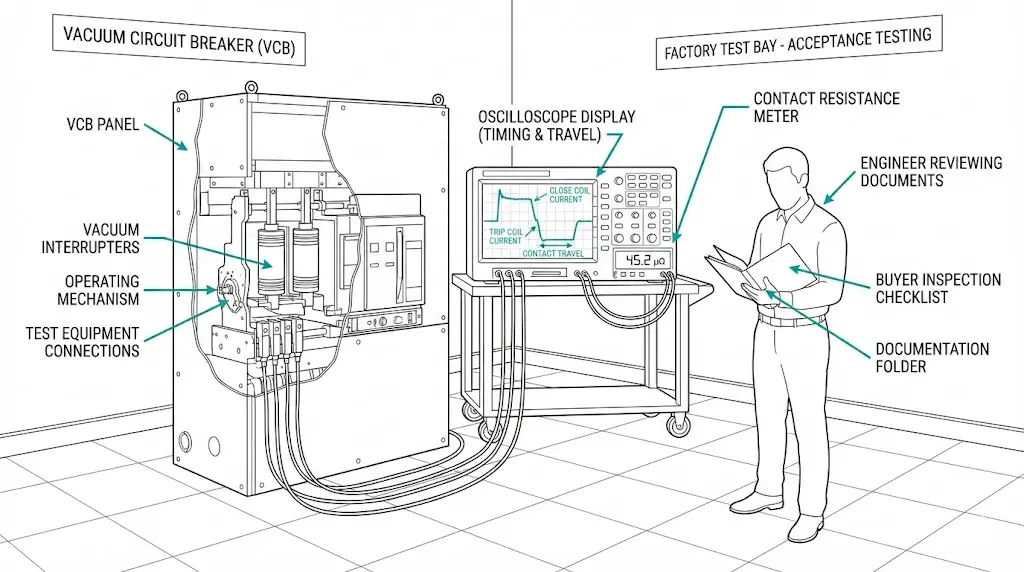
A procurement engineer walks into the manufacturer’s test bay. Three vacuum circuit breaker panels stand ready for inspection. The test engineer presents a documentation folder—but is everything inside?
Missing documents at Factory Acceptance Test create problems that compound through the project lifecycle. An absent type test certificate delays shipment. Incomplete routine test records trigger disputes during commissioning. A mismatched serial number invalidates warranty claims years later.
This guide delivers the complete FAT/SAT acceptance framework for vacuum circuit breaker procurement. You will find document checklists, test sheet parameters with acceptance thresholds, and a buyer sign-off protocol ready for your next factory visit or site commissioning.
A FAT/SAT acceptance pack for VCB equipment represents the complete documentation portfolio that validates vacuum circuit breaker performance before shipment and after site installation. For procurement engineers evaluating medium-voltage switchgear, this acceptance pack serves as contractual evidence that your vacuum circuit breaker meets specified ratings—typically covering breaking capacities from 25 kA to 50 kA at voltage classes of 12 kV, 24 kV, or 36 kV.
Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) occurs at the manufacturer’s facility where specialized test equipment validates the vacuum interrupter’s arc extinction capability. Synthetic test circuits capable of generating 100 kA peak asymmetrical current verify breaking performance under controlled conditions. Site Acceptance Test (SAT) then confirms that transportation, handling, and installation have not compromised operational integrity.
The distinction matters. FAT catches manufacturing defects before equipment leaves the factory. SAT identifies transport damage, installation errors, and site-specific issues before energization.
| Parameter | FAT | SAT |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Manufacturer’s test bay | Project site |
| Timing | Before shipment | After installation |
| Primary Purpose | Verify manufacturing quality | Confirm installation integrity |
| Witnesses | Buyer representative (optional) | Buyer + commissioning engineer |
| Documents Generated | Type test certs, routine test records | Insulation tests, relay coordination |

The acceptance pack documentation structure follows requirements outlined in IEC 62271-100 for high-voltage switchgear and controlgear, which mandates type test reports, routine test certificates, and instruction manuals as minimum deliverables. For buyers working with vacuum circuit breaker manufacturers, requesting this complete documentation set upfront prevents delays during project execution.
A complete FAT package contains five document categories. Each serves a distinct verification purpose.
Type Test Certificates validate that the VCB design meets dielectric withstand requirements, short-circuit breaking capacity, and mechanical endurance limits. These certificates apply to the product design—not the individual unit. Verify that the certificate model designation exactly matches your purchase order. A certificate for “VCB-12/630-25” does not cover “VCB-12/1250-31.5.”
Routine Test Records document tests performed on every manufactured unit. According to IEC 62271-100, routine tests include:
Material Certificates provide traceability for critical components. Vacuum interrupter batch numbers, copper-chromium contact alloy certifications, and epoxy insulation material specifications become essential for warranty claims and failure analysis.
Assembly Drawings and Wiring Diagrams include single-line diagrams, control circuit schematics, and terminal designations per IEC 60617 symbols. Specify drawing format requirements in your purchase contract—manufacturers may default to local standards that create interpretation issues during commissioning.
Operation and Maintenance Manuals must be provided in the contract-specified language. These documents include maintenance schedules, lubrication points, spare parts lists, and storage instructions for extended warehouse periods.
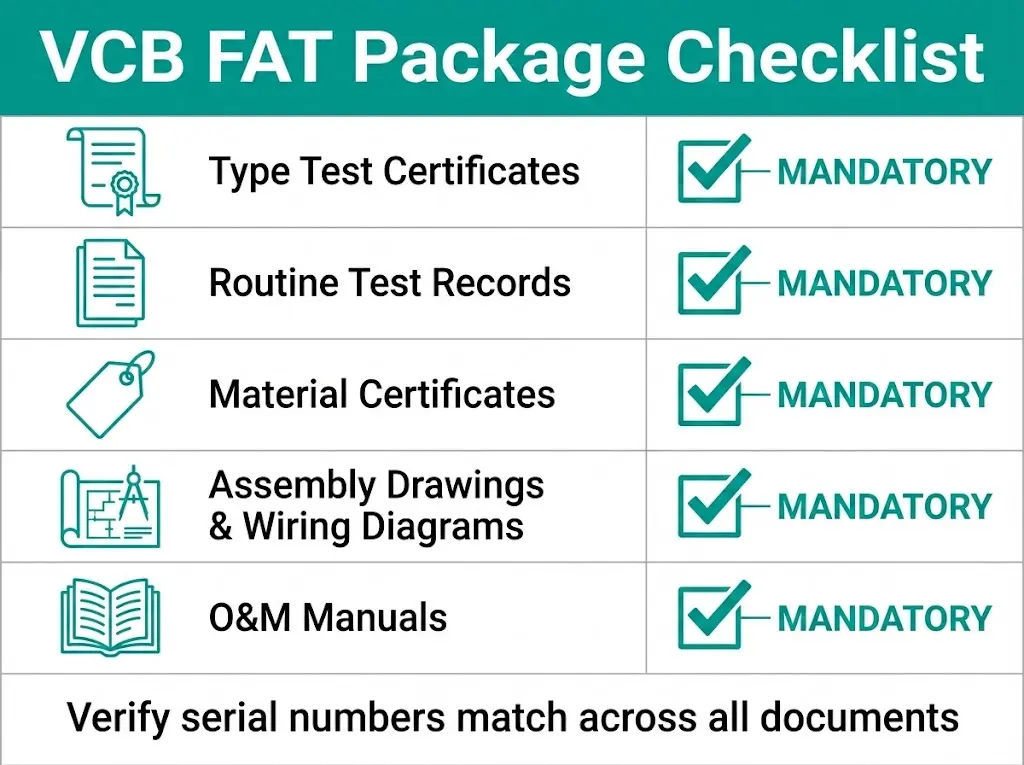
| Document | Classification | Verification Point |
|---|---|---|
| Type Test Certificate | Mandatory | Model designation matches PO |
| Routine Test Records | Mandatory | Serial number matches unit |
| Material Certificates | Mandatory | Traceability to component batch |
| Assembly Drawings | Mandatory | Current revision, correct language |
| O&M Manual | Mandatory | Contract language, complete content |
| Factory Photos | Optional | Visual record of assembly |
[Expert Insight: FAT Document Verification]
- Request type test certificate copies 2 weeks before your FAT visit to verify model match
- Check routine test record dates—tests performed months before your visit may indicate refurbished stock
- Confirm material certificate batch numbers appear on actual vacuum interrupter nameplates
- Photograph all nameplates during FAT for permanent project records
Understanding the physics behind each routine test enables buyers to evaluate results meaningfully rather than simply checking boxes.
Power-Frequency Withstand Voltage Test verifies main insulation dielectric strength. The test applies voltage for one minute across open contacts and between phases and ground. For 12 kV rated VCB, test voltage reaches 28 kV power-frequency and 75 kV lightning impulse [VERIFY STANDARD: IEC 62271-1 Table 2 for exact values by voltage class]. Pass criteria: no flashover, no sustained partial discharge.
Contact Resistance Measurement confirms low I²R losses at rated current. The test injects minimum 100 A DC through main contacts while measuring voltage drop. For 12 kV class VCB with new contacts, acceptable values fall below 50 μΩ per phase. Higher readings indicate contact surface contamination, insufficient pressure, or manufacturing defects. This parameter directly affects temperature rise during continuous current operation.
Timing Test measures opening time, closing time, and phase simultaneity. Spring-operated 12 kV VCB typically shows:
Timing affects protection coordination. An unexpectedly slow breaker may fail to clear faults within upstream relay coordination margins.
Vacuum Interrupter Integrity Check confirms the arc-extinguishing medium remains below required pressure threshold—typically 10⁻² Pa. Two methods apply:
For deeper understanding of the vacuum arc extinction process, review the working principle of vacuum circuit breakers.
Site conditions differ fundamentally from factory test bays. Temperature variations, humidity, altitude, and contamination affect insulation performance. Transportation introduces mechanical stress. Installation introduces human error.
Pre-Commissioning Visual Inspection catches transport damage before electrical testing. Check for:
Insulation Resistance Measurement uses a 5 kV DC megger for 12 kV class equipment. Acceptable readings exceed 1,000 MΩ at 20°C ambient. Temperature and humidity affect results—coastal installations during monsoon season may show lower readings requiring temperature correction. Document ambient conditions alongside measured values.
Primary Injection Test verifies CT ratio and polarity using a high-current test set. This confirms that protection relays receive correct current magnitude and phase relationship. Reversed CT polarity causes directional protection maloperation.
Protection Relay Coordination Verification uses secondary injection to confirm trip settings match the coordination study. Document actual pickup values and compare against design specification.
Interlock and Control Circuit Test verifies:

For installations above 1,000 m altitude, apply derating factors to insulation test voltage levels. High-altitude sites experience reduced air density, lowering external flashover thresholds. The indoor vs outdoor VCB selection guide addresses environmental considerations in detail.
[Expert Insight: SAT Field Realities]
- Schedule SAT during stable weather—rain delays outdoor switchyard testing by days
- Bring backup megger batteries; site power may be unavailable during pre-commissioning
- Low insulation readings after sea shipment often recover after 24-48 hours in dry conditions
- Photograph every nameplate and test setup for dispute resolution records
The sign-off checklist transforms acceptance testing from observation into contractual commitment. Once signed, responsibility transfers from manufacturer to buyer.
Document Completeness Verification confirms every FAT package element is present, correctly dated, and matched to unit serial numbers. Use a matrix format:
| Document | Present | Serial Match | Current Rev | Sign-off |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type Test Cert | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | _______ |
| Routine Test Record | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | _______ |
| Material Certs | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | _______ |
| Drawings | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | _______ |
| O&M Manual | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | _______ |
Visual Inspection Sign-off covers nameplate accuracy, paint finish quality, bushing condition, and mechanism handle function. Operate the manual close/open handle during FAT witness—this reveals binding or misalignment before shipping.
Test Witness Confirmation documents your presence during routine testing. Most contracts allow buyer witness rights with 2–4 weeks advance scheduling. Bring your purchase order copy, technical specification, and camera. Some manufacturers require witness attendance documentation for warranty activation.
Non-Conformance Report (NCR) Handling addresses test failures or documentation gaps:
Before FAT attendance, prepare using the VCB RFQ checklist to verify purchase order completeness.

Field experience across dozens of VCB acceptance tests reveals recurring problems. Anticipating these deficiencies prevents schedule impact.
Missing or Mismatched Type Test Certificates rank as the most frequent FAT deficiency. Manufacturers sometimes provide certificates for similar models rather than the exact variant ordered. Prevention: specify exact model designation in purchase order and request certificate copy before travel.
Timing Deviations Beyond Tolerance indicate mechanism adjustment issues, spring fatigue, or lubricant degradation. Factory-fresh VCB showing out-of-tolerance timing warrants investigation before acceptance. Prevention: witness timing test personally and require re-adjustment plus retest if borderline.
Documentation Language and Format Issues create commissioning delays when manuals arrive in languages your maintenance team cannot read or drawings use unfamiliar symbol standards. Prevention: specify documentation language and drawing standard (IEC 60617) explicitly in purchase contract.
Transport Damage Discovered at SAT represents the costliest deficiency—equipment already shipped, installation complete, then damage found. Cracked bushings from vibration, moisture ingress from inadequate packaging, or mechanism misalignment from rough handling require manufacturer assessment and potential return shipment. Prevention: specify packaging requirements, require shipping insurance, and conduct receiving inspection before installation.
XBRELE provides vacuum circuit breakers with comprehensive FAT/SAT acceptance packs meeting international procurement standards. Our documentation package includes:
Technical support extends beyond delivery. Our commissioning guidance assists your team through SAT execution, and field service engineers remain available for complex installation scenarios.
Contact XBRELE for VCB quotations that include acceptance documentation specifications matched to your project requirements.
External Reference: IEC 60071 — IEC 60071 insulation coordination
What is the difference between FAT and SAT for vacuum circuit breakers?
FAT verifies manufacturing quality at the factory before shipment, while SAT confirms that transportation and installation have not degraded performance at the project site—both stages catch different defect categories.
How far in advance should buyers schedule FAT witness attendance?
Most manufacturers require 2–4 weeks advance notice for witness test scheduling, though complex projects with multiple VCB panels may need 6+ weeks to coordinate production sequences with buyer availability.
What contact resistance value indicates a problem in a new 12 kV VCB?
Readings above 50 μΩ per phase warrant investigation; values exceeding 80 μΩ typically require contact surface inspection or mechanism pressure adjustment before acceptance.
Can FAT documentation substitute for SAT testing?
No—SAT specifically verifies that transportation, handling, and installation have not introduced new defects; factory test results cannot predict post-shipment condition.
What recourse exists if the manufacturer refuses to correct FAT deficiencies?
Buyers may withhold payment milestone release, invoke contract penalty clauses, or escalate to formal dispute resolution; document all deficiencies photographically and in writing during the FAT visit.
How long should VCB acceptance documentation be retained?
Retain complete FAT/SAT records for the equipment’s entire service life—typically 20–30 years—as these documents support warranty claims, failure investigations, and eventual replacement planning.
Does altitude affect SAT test acceptance criteria?
Yes—installations above 1,000 m require derating factors for insulation test voltages and may show different thermal performance; reference manufacturer altitude correction tables during SAT evaluation.