Need Full Specifications?
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Ring main units form the backbone of medium-voltage secondary distribution—compact, modular, and engineered for decades of unattended operation. For utility engineers and industrial buyers, RMU manufacturer selection extends far beyond the initial purchase. You’re committing to a 25-year relationship involving spare parts, service support, and technology compatibility.
This guide delivers what most RMU articles overlook: a structured manufacturer evaluation framework paired with practical LBS/fuse configuration strategy. Whether you’re building a shortlist for urban cable networks or selecting protection schemes for transformer feeders, the sections ahead connect manufacturer capabilities to real application requirements.
The 2026 market adds urgency. SF₆-free designs now dominate tender specifications across Europe and are gaining ground throughout Asia-Pacific and Middle East markets. Your shortlist must account for this shift.
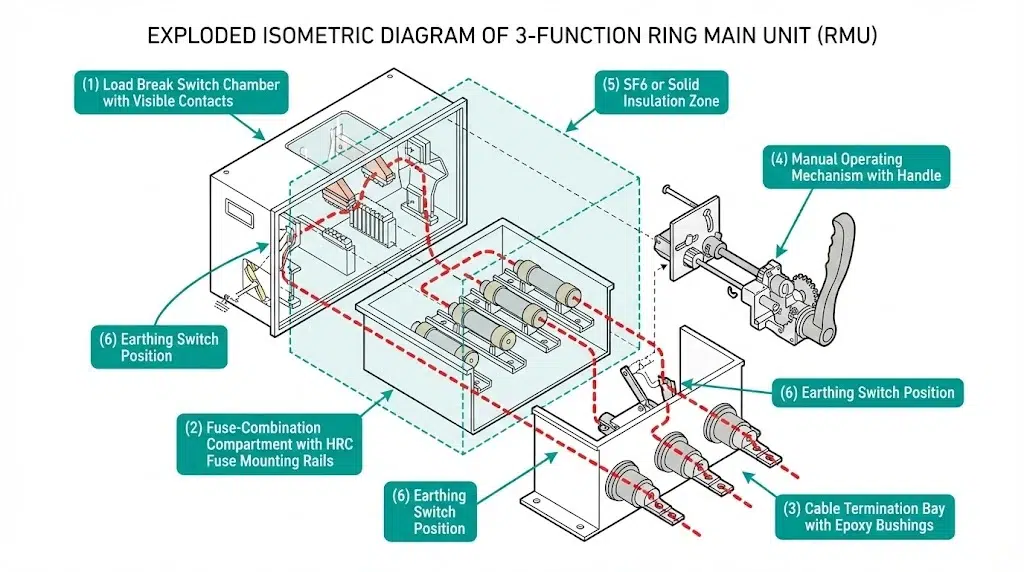
A ring main unit is a factory-assembled, type-tested switchgear assembly designed for secondary MV distribution networks operating at 12 kV, 24 kV, or up to 36 kV. Unlike panel-built switchgear, RMUs arrive as sealed or semi-sealed modules—ready for cable termination with minimal on-site work.
Core Functions:
Typical Specifications:
RMUs are not commodity products. Three factors make manufacturer choice a long-term decision:
Asset lifespan typically reaches 25–35 years. Your supplier must maintain spare parts availability and technical support across this entire horizon. Network dependency means a failed module affects multiple downstream customers—manufacturer quality directly impacts reliability metrics like SAIDI and SAIFI. Technology lock-in occurs because extensible RMU designs allow adding modules over time, but only from the same manufacturer. Limited product ranges restrict future flexibility.
Selecting the right RMU manufacturer requires evaluating technical capabilities that directly impact network reliability and total cost of ownership.
1. Type Test Certification
Verify IEC 62271-200 compliance through accredited third-party laboratories—CESI, KEMA, or XIHARI. Self-declared compliance without independent verification should raise immediate concerns. According to IEC 62271-200 clause 6.106, internal arc classification (IAC) testing must demonstrate personnel protection during fault events, with arc containment times typically specified at 0.5 s or 1.0 s at fault currents up to 25 kA.
2. Manufacturing Depth
Distinguish between genuine manufacturers and assembly operations. Vertical integration—in-house vacuum interrupter production, enclosure fabrication, insulation molding—indicates manufacturing depth. During factory acceptance testing, manufacturers with in-house vacuum interrupter production consistently achieve tighter partial discharge thresholds: typically below 5 pC at 1.2 × rated voltage compared to 10 pC from assembled-component suppliers.
3. SF₆-Free Portfolio
Availability of solid dielectric or clean-air alternatives has become mandatory for European tenders and increasingly expected elsewhere. Manufacturers without credible SF₆-free roadmaps face shrinking addressable markets.
4. Service Network and Spare Parts
Regional presence determines response time during failures. Critical components—operating mechanisms, fuse-striker assemblies, pressure gauges—should ship within 72 hours for priority orders. Confirm spare parts commitments extending 15–20 years minimum.
5. Reference Installations
Request contactable references in similar climate and application conditions. Track record matters more than brochure specifications.

[Expert Insight: Factory Audit Red Flags]
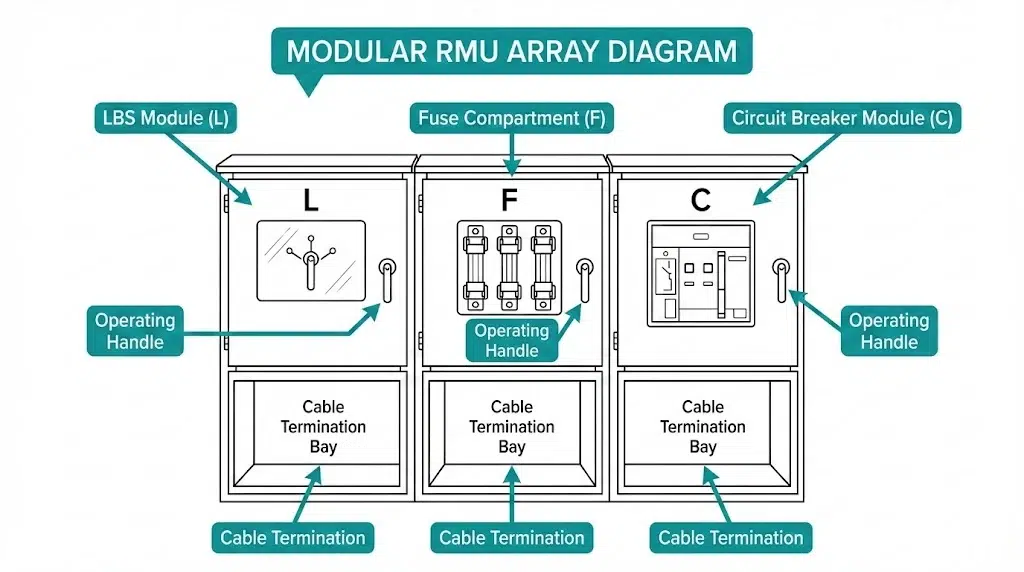
Understanding functional module designations enables informed configuration decisions. Modern RMUs combine three primary module types in various arrangements.
L — Load Break Switch Module
The L module provides ring circuit isolation and load current switching up to 630 A continuous. It handles load transfer between cable feeders but cannot interrupt fault currents. Standards compliance follows IEC 62271-103. Typical ratings: 12 kV/24 kV, 630 A, 20 kA short-time withstand for 3 seconds.
C — Circuit Breaker Module
The C module delivers full fault interruption capability via vacuum interrupter technology. Breaking capacities reach 20–25 kA at 12 kV or 24 kV. This module enables auto-reclosing schemes and sophisticated protection coordination. Standards compliance follows IEC 62271-100.
F — Fuse-Combination Switch Module
The F module combines a load break switch with high-voltage fuses for transformer protection. When a fuse operates, its striker mechanism triggers the LBS to open, isolating the faulted circuit. This cost-effective solution suits transformers up to 630 kVA. Standards compliance follows IEC 62271-105.
Common Configurations:
Extensible designs allow adding modules as network requirements evolve—but only using the same manufacturer’s components. Non-extensible compact units suit fixed configurations where future expansion is unlikely.
For applications requiring SF6 load break switch technology, manufacturers should demonstrate proven gas-handling expertise and leak rate performance below IEC thresholds.
The regulatory landscape has shifted decisively. EU F-gas Regulation 517/2014, strengthened in 2024, restricts SF₆ use in new medium-voltage switchgear. SF₆ carries global warming potential 23,500 times that of CO₂—making phase-down inevitable across major markets.
| Technology | Insulation Medium | Switching Medium | Maintenance Profile | Market Trajectory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF₆ Gas | SF₆ | SF₆ puffer or vacuum | Gas monitoring required | Declining—EU restricted |
| Solid Dielectric | Epoxy/silicone resin | Vacuum | Sealed-for-life | Growing rapidly |
| Dry Air | Pressurized atmospheric air | Vacuum | Minimal monitoring | Schneider AirSeT series |
| Clean Air Mix | Air + CO₂ mixture | Vacuum | Minimal monitoring | Siemens Blue GIS |
SF₆-free alternatives now meet or exceed performance requirements for voltages up to 36 kV. Solid dielectric RMUs achieve maintenance-free operation exceeding 25 years under normal service conditions—eliminating quarterly gas-quality checks required for SF₆ units.
Total cost of ownership often favors SF₆-free despite higher acquisition costs. Gas handling equipment, monitoring systems, and end-of-life recovery add substantial lifecycle expenses to SF₆ installations.
For detailed regulatory context, refer to the EU F-gas Regulation documentation outlining phase-down schedules and exemption criteria.
Schneider Electric dominates market share with the SM6 and RM6 series. The SM AirSeT represents their flagship SF₆-free platform using dry air insulation. Strong global service networks and extensive installed base provide proven reliability data.
Siemens offers the 8DJH series with Blue GIS technology employing clean air and vacuum switching. German engineering heritage translates to rigorous quality systems. Particularly strong in European and Middle Eastern utility networks.
ABB/Hitachi Energy pioneered solid dielectric technology with SafeRing, SafePlus, and SafeLink platforms. Shielded solid insulation eliminates gas handling entirely. Vacuum interrupter integration delivers 25 kA breaking capacity in compact footprints.
Eaton produces the Xiria series—fully SF₆-free from inception. Modular extensibility accommodates network growth. Strong presence in European renewable energy installations.
Lucy Electric (UK) serves EMEA and Asian markets with Aegis, Sabre, and Gemini series. IP67-rated enclosures suit tropical and flood-prone installations. Both SF₆ and solid dielectric options available.
Ormazabal (Spain) offers the cgmcosmos series with extensive European installed base. Competitive pricing for utility-scale deployments. Part of Velatia group.
Toshiba (Japan) provides VRV series vacuum-based RMUs with strong Asia-Pacific presence. Proven reliability in high-humidity environments.
Chinese manufacturers—Changgao, Senyuan, Pinggao, and regional specialists—offer competitive pricing at 40–60% below Tier 1 costs. Quality has improved significantly, with some products achieving 8,000+ switching operations without contact degradation in mining applications.
Due diligence remains essential: verify IEC type test reports from accredited laboratories, conduct factory audits before volume orders, and confirm spare parts availability outside China.

[Expert Insight: Evaluating Chinese RMU Suppliers]
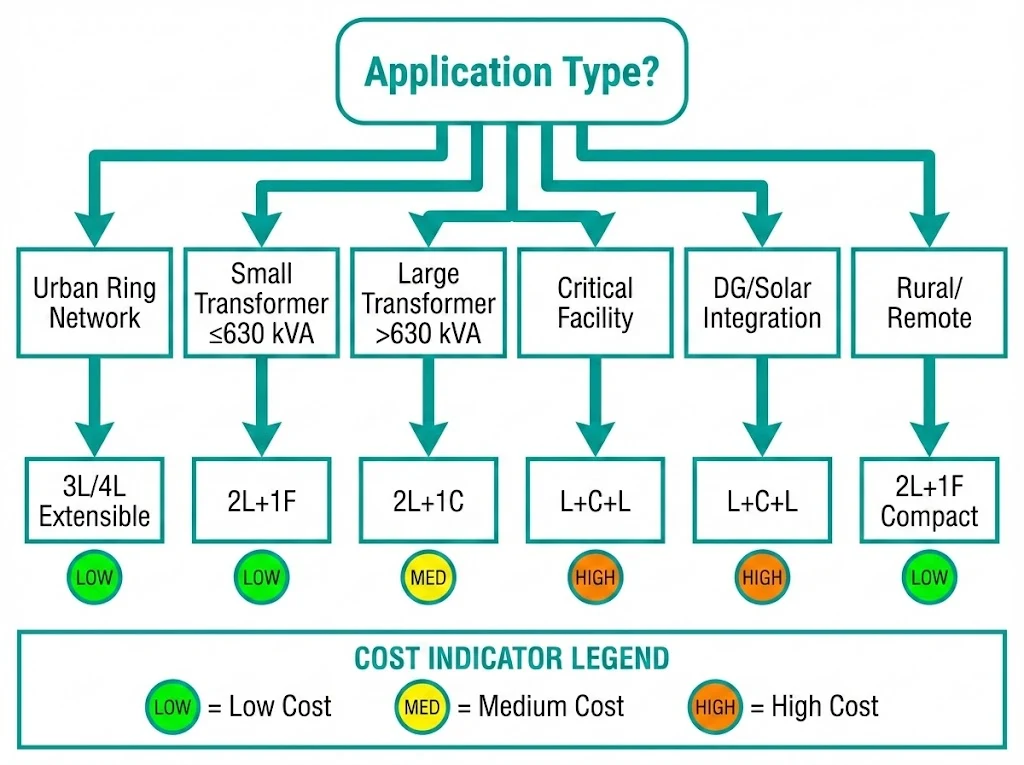
Configuration selection must match application requirements. Load-break switches handle rated currents up to 630 A with fault-making capacity reaching 20 kA, while fuse-protected circuits provide breaking capacities exceeding 40 kA through high-rupturing-capacity (HRC) fuses.
| Application | Recommended Configuration | Protection Type | Auto-Reclosing | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban ring network | 3L or 4L extensible | Ring isolation only | N/A | Medium |
| Small transformer (≤630 kVA) | 2L+1F | HRC fuse | No | Low |
| Large transformer (>630 kVA) | 2L+1C | CB + protection relay | Optional | High |
| Critical facility (hospital, data center) | L+C+L | Full circuit breaker | Yes | High |
| Distributed generation (solar, wind) | L+C+L | Directional CB protection | Yes | High |
| Rural/remote feeder | 2L+1F compact | HRC fuse | No | Low |
Field experience across 120+ urban distribution substations confirms that fuse-protected configurations suit transformers up to 630 kVA where auto-reclosing is unnecessary. Above this threshold—or for critical loads—circuit breaker modules justify their cost premium through protection coordination flexibility and remote operation capability.
In coastal installations with salt-fog exposure, solid dielectric RMUs demonstrate measurably lower maintenance burden. No gas monitoring, no seal inspections—compared to SF₆ units requiring quarterly pressure checks in corrosive environments.
When specifying switchgear components for RMU applications, ensure compatibility with both current network fault levels and projected growth scenarios.
Before issuing requests for quotation, systematic verification prevents costly specification errors.
Technical Verification:
Configuration Compatibility:
Environmental Suitability:
Commercial and Support Terms:
For circuit breaker modules, verify vacuum circuit breaker specifications including contact erosion rates and mechanical endurance ratings.
XBRELE supplies OEM components for RMU manufacturers and system integrators worldwide. Our product range supports both SF₆ and SF₆-free RMU designs:
Type-tested components with third-party certification from accredited laboratories ensure compliance verification. OEM/ODM capability accommodates custom specifications for regional standards and utility preferences.
Engineering support extends from initial enquiry through production, including protection coordination consultation and arc flash calculation assistance.
Request a quotation for RMU-compatible vacuum interrupters, LBS assemblies, and switchgear components—backed by IEC type testing and dedicated technical support.
Q: What does RMU stand for in electrical distribution?
A: RMU stands for Ring Main Unit—a compact, factory-sealed switchgear assembly used in medium-voltage networks to connect cable ring circuits and protect distribution transformers, typically rated between 12 kV and 36 kV.
Q: How do I choose between fuse protection (F) and circuit breaker © modules?
A: Fuse-combination modules suit transformers up to 630 kVA where auto-reclosing is unnecessary and cost optimization matters; circuit breaker modules serve larger transformers, critical loads, or applications requiring remote operation and sophisticated protection coordination.
Q: Why are utilities transitioning away from SF₆-insulated RMUs?
A: SF₆ has global warming potential 23,500 times greater than CO₂, prompting regulatory restrictions in Europe and elsewhere; SF₆-free alternatives using vacuum switching with solid or air insulation now achieve comparable performance while eliminating gas handling requirements and environmental liability.
Q: What type test certifications should I verify from RMU manufacturers?
A: Request IEC 62271-200 compliance certificates from accredited third-party laboratories such as CESI, KEMA, or XIHARI; verify internal arc classification ratings and ensure short-circuit withstand values match your network fault levels.
Q: How long do RMUs typically remain in service?
A: Well-maintained RMUs achieve service lives of 25–35 years; solid dielectric designs often operate maintenance-free for 25+ years, while SF₆ units require periodic gas monitoring throughout their operational life.
Q: What questions should I ask Chinese RMU manufacturers during evaluation?
A: Request type test certificates from internationally recognized laboratories, verify production capabilities through factory audits, confirm spare parts availability and lead times for export markets, and obtain contactable reference installations from utilities outside the manufacturer’s home region.
Q: Can I expand an existing RMU installation with additional modules?
A: Extensible RMU designs accommodate future module additions, but only from the same manufacturer; confirm extensibility options and long-term product availability before initial purchase if network growth is anticipated.