Need Full Specifications?
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
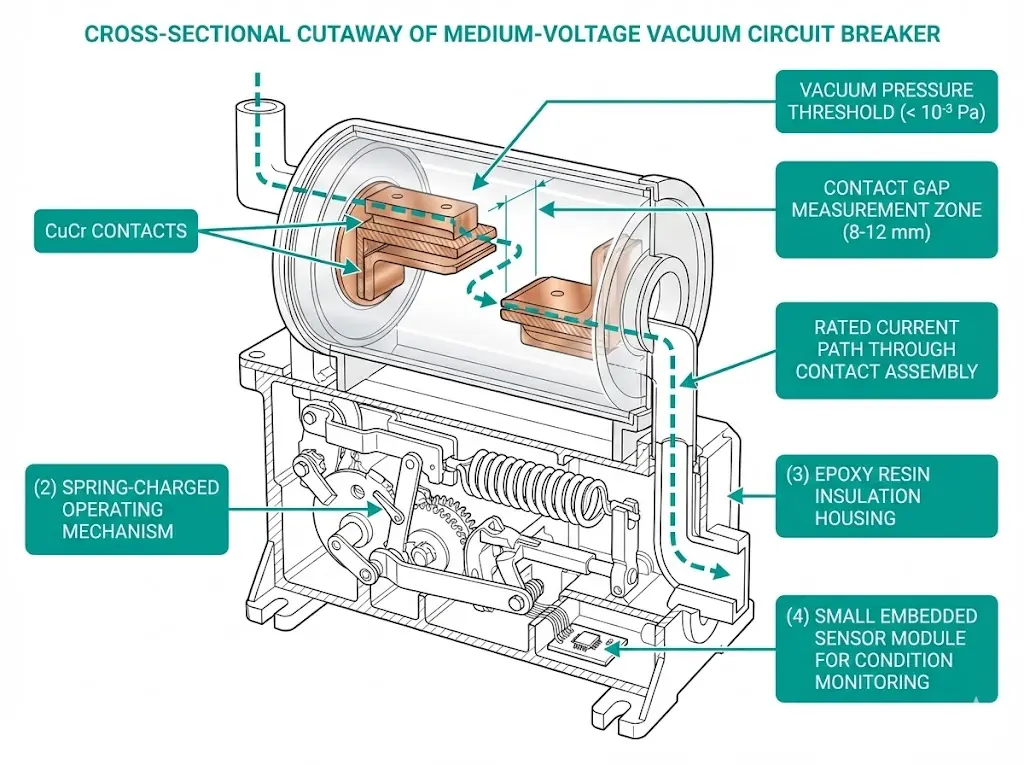
A vacuum circuit breaker installed today will still protect your network in 2050. That 25-year horizon makes manufacturer selection one of the most consequential decisions in medium-voltage procurement. The interrupter inside will execute tens of thousands of switching operations. The mechanism will clear faults in under 60 milliseconds. The insulation system will face humidity, temperature extremes, and contamination you cannot fully predict at commissioning.
Two breakers carrying identical ratings—12 kV, 630 A, 25 kA—can diverge dramatically over service life. Contact erosion rates vary by a factor of two between manufacturers using different CuCr alloy formulations. Spring mechanism MTBF differs by 15,000 operations or more. Spare part availability ranges from 48-hour regional delivery to 12-week international shipments.
This guide delivers two things: a qualified shortlist of vacuum circuit breaker manufacturers with demonstrated MV capability, and a scoring framework that converts subjective brand preference into quantifiable comparison.
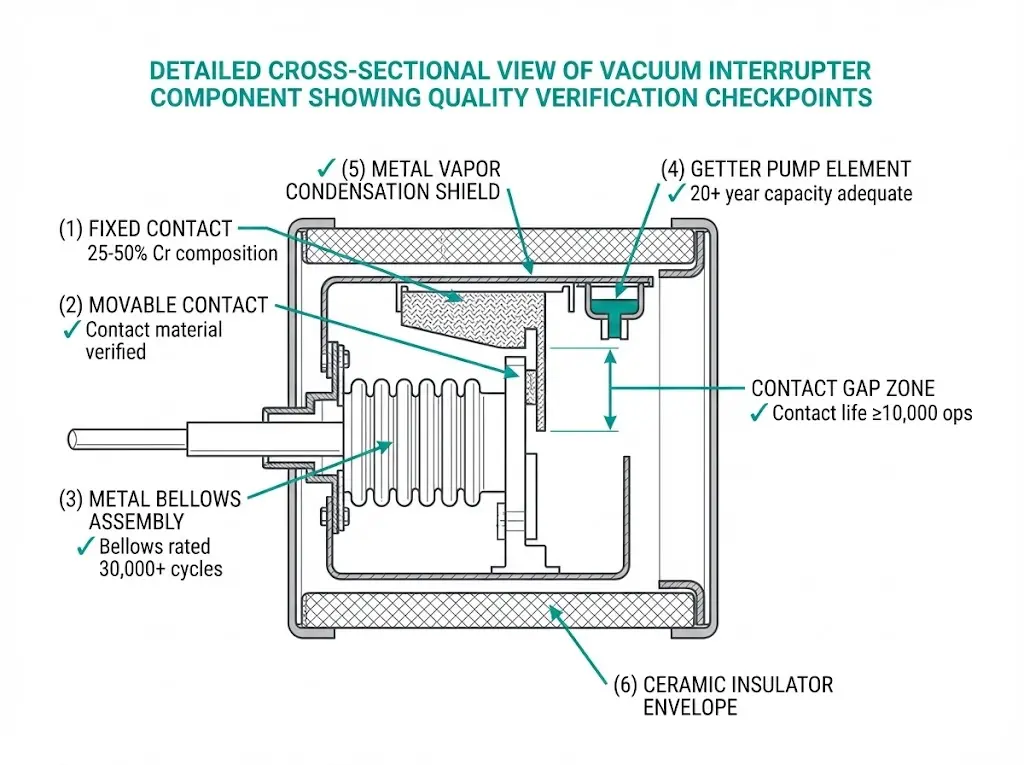
In assessments across 75+ industrial substations and utility installations, we have observed that vacuum circuit breaker performance varies substantially between manufacturers—even when products carry identical voltage ratings. The difference traces to vacuum interrupter quality, where internal pressure must remain below 10⁻³ Pa throughout a 20–30 year service life to maintain reliable arc quenching.
According to IEC 62271-100, these switching devices must interrupt symmetrical fault currents up to 50 kA at rated voltages between 12 kV and 40.5 kV, while maintaining contact erosion rates permitting at least 10,000 mechanical operations. Meeting these thresholds requires manufacturing precision that not all suppliers achieve consistently.
Three factors drive manufacturer differentiation:
Vacuum Interrupter Technology: CuCr contact composition and production precision directly affect chopping current levels (typically 3–5 A for quality units) and dielectric strength recovery after arc extinction.
Digital Integration: Leading manufacturers now embed condition monitoring sensors tracking vacuum integrity, contact wear, and mechanism health—essential for predictive maintenance.
Application-Specific Engineering: Mining substations, renewable energy installations, and marine applications each demand distinct environmental ratings. Ingress protection from IP54 to IP67 and operating temperatures spanning -40°C to +55°C separate general-purpose units from harsh-environment designs.
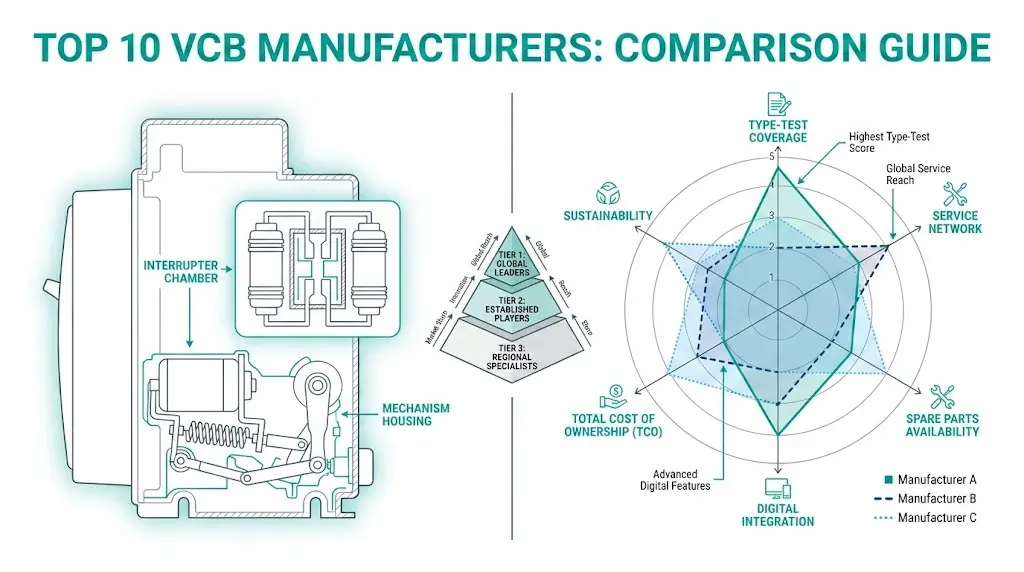
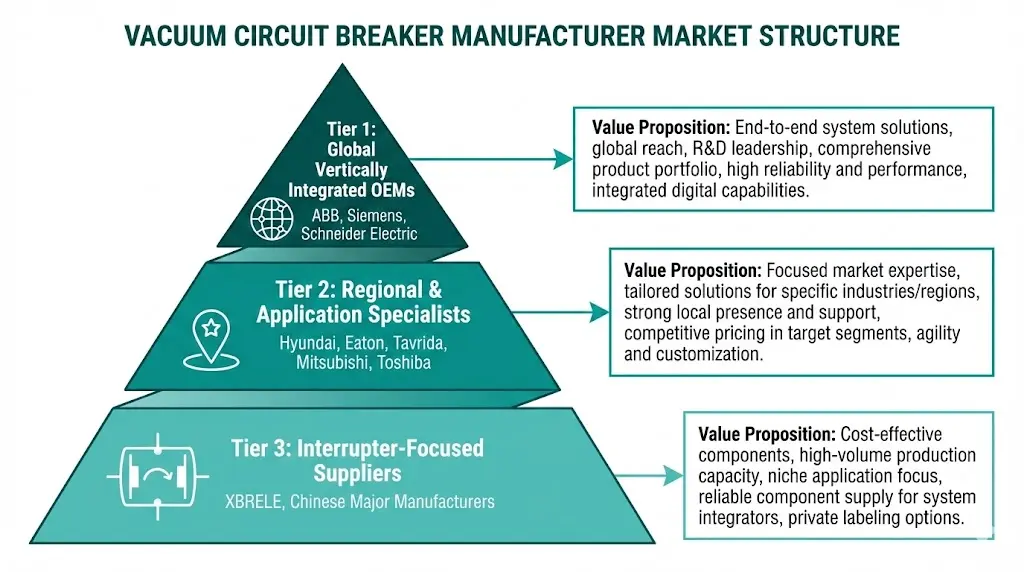
Tier 1 — Global Vertically Integrated OEMs
Companies like ABB, Siemens, and Schneider Electric manufacture vacuum interrupters in-house and produce complete switchgear assemblies. They maintain global service networks, hold extensive type-test portfolios, and price at premium levels.
Tier 2 — Regional and Application Specialists
Manufacturers with strong positions in specific geographies (Hyundai Electric in Asia, Eaton in North America) or applications (Tavrida Electric in reclosers). Often competitive on price with focused technical depth.
Tier 3 — Interrupter-Focused Suppliers
Companies manufacturing vacuum interrupters for panel builders who assemble complete breakers. XBRELE operates here with vertically integrated interrupter production and complete VCB offerings.
Your optimal tier depends on project scale, voltage class, service network requirements, and whether you need turnkey solutions or component supply.
The VD4 platform remains one of the most widely installed indoor VCB designs globally. ABB manufactures interrupters in-house, offering breakers rated to 40.5 kV and 50 kA breaking capacity.
Strengths: Extensive IEC 62271-100 documentation, global service network with regional spare part hubs, digital integration via ABB Ability sensors.
Considerations: Premium pricing; extended lead times observed during 2022–2023 supply disruptions.
The SION series and 3AH/3AF lines serve utility-scale distribution from 10–24 kV. Siemens maintains one of Europe’s largest vacuum interrupter R&D operations.
Strengths: Proven utility performance, strong European grid code compliance, SF₆-free hybrid options (Blue GIS range).
Considerations: Complex product portfolio requires careful specification; service contracts can exceed equipment cost over 15-year lifecycle.
Evolis and EasyPact MVS platforms cover 7.2–24 kV applications, emphasizing compact designs for urban substations and commercial buildings.
Strengths: Strong building and light industrial presence, modular RMU integration, comprehensive distributor training programs.
Considerations: Less penetration in heavy industrial and mining segments.
VCP-W and Pow-Vac lines demonstrate particular strength in ANSI-rated North American markets.
Strengths: Deep ANSI/IEEE compliance (C37.04, C37.09 protocols), established retrofit ecosystem, strong Americas utility relationships.
Considerations: Narrower IEC-rated product line; limited presence in Asian and African markets.
In-house vacuum interrupter manufacturing at Japanese facilities, with licensed production across Asia. Serves utility and industrial markets.
Strengths: High manufacturing precision with low interrupter seal defect rates, proven coastal and high-humidity performance.
Considerations: Service network thinner outside Asia-Pacific; documentation sometimes requires translation.
Utility transmission and distribution focus, with rated voltages extending to 36 kV.
Strengths: Vertically integrated interrupter production, seismic-rated designs for Pacific Rim installations, long-term component availability commitments.
Considerations: Smaller market share outside Japan and Southeast Asia.
Utility, industrial, and marine applications from consolidated South Korean manufacturing.
Strengths: Competitive IEC-compliant pricing, strong shipbuilding and offshore platform expertise, growing global utility references.
Considerations: Service network still developing in Africa and South America.
Specializes in outdoor vacuum reclosers and indoor VCBs with embedded protection relays.
Strengths: Recloser technology leadership with 30,000+ operation mechanical endurance, integrated protection electronics, competitive total cost of ownership.
Considerations: Narrower product range than full-line OEMs; lower brand recognition outside recloser applications.
Vertically integrated manufacturer producing CuCr vacuum interrupters and complete VCBs for 12–40.5 kV applications.
Strengths: In-house interrupter production with controlled CuCr metallurgy, competitive export pricing, flexible OEM/ODM arrangements for panel builders.
Considerations: Brand building ongoing in some export markets; buyers should verify specific type-test reports for target applications.
Large domestic producers expanding internationally through Belt & Road infrastructure projects.
Strengths: Aggressive pricing for standard specifications, high production capacity enabling short lead times, growing international certification coverage.
Considerations: Quality varies between manufacturers—due diligence essential; service support outside China requires explicit contractual definition.
[Expert Insight: Evaluating Tier 2 and Tier 3 Manufacturers]
- Request actual type-test certificates, not data sheet summaries—verify the tested model matches your specified variant
- For interrupter suppliers, confirm CuCr alloy composition falls within 25–50% chromium range
- Check manufacturing location: some brands badge products from multiple factories with varying quality systems
- Prioritize suppliers with regional service depots over those requiring international spare part shipments
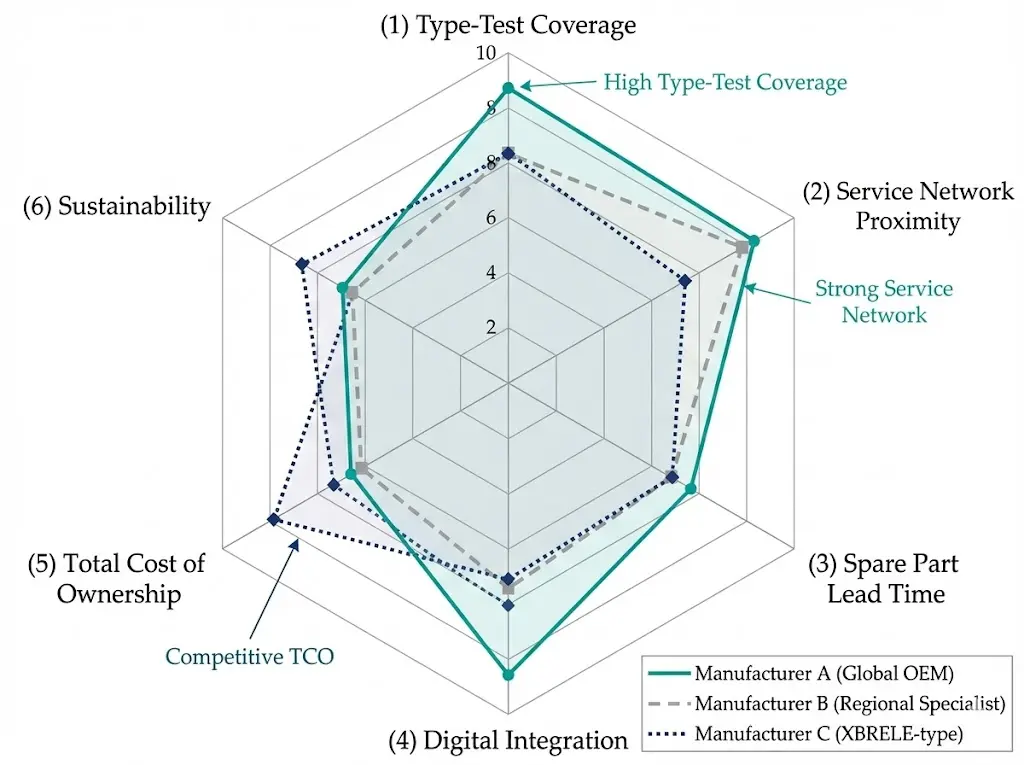
Converting brand preference into objective comparison requires structured scoring. The framework below weights criteria by their impact on long-term operational reliability.
| Criterion | Weight | Scoring Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Type-Test Coverage | 20% | Full IEC 62271-100 or ANSI C37 for your rating = 10 pts; partial = 5 pts; none = 0 |
| Interrupter Technology | 15% | In-house VI production = 10 pts; established supplier = 7 pts; unknown source = 3 pts |
| Service Network Proximity | 15% | Depot < 500 km = 10 pts; regional hub < 2,000 km = 6 pts; central factory only = 2 pts |
| Spare Part Lead Time | 10% | < 2 weeks = 10 pts; 2–6 weeks = 6 pts; > 6 weeks = 3 pts |
| Reference Installations | 10% | Similar application, voltage, and environment within 5 years = 10 pts |
| Digital Integration | 10% | Native IEC 61850 + embedded sensors = 10 pts; retrofit options = 6 pts; none = 2 pts |
| Total Cost of Ownership | 10% | 15-year lifecycle model: acquisition + service + spares + training |
| Commercial Terms | 5% | Payment terms, warranty duration, penalty clauses |
| Sustainability | 5% | SF₆-free or low-GWP insulation options = bonus points |
Beyond manufacturer reputation, verify these parameters for the specific breaker model under consideration.
[Expert Insight: Field Verification Lessons]
- Altitude above 2,000 m reduces dielectric strength by approximately 1% per 100 m—verify manufacturer’s derating calculations
- In coastal installations, request salt fog test documentation (IEC 60068-2-11) beyond standard type-tests
- Operating mechanism stored energy degrades over time; specify minimum acceptable values at end-of-life, not just commissioning
- Contact gap measurements during routine maintenance should remain within ±5% of factory specification
Five recurring mistakes observed across utility and industrial VCB procurement:
1. Accepting “equivalent” substitutions without requalification
A different breaker model—even from the same manufacturer—requires full technical review. Type-test certificates are model-specific.
2. Ignoring lifecycle costs
A breaker priced 30% lower at acquisition can cost 50% more over 15 years if spare parts require intercontinental shipping during outages.
3. Over-specifying breaking capacity
Demanding 50 kA when network fault levels reach 25 kA maximum wastes budget and may introduce unnecessary mechanism complexity.
4. Under-specifying environmental conditions
Installations above 2,000 m or in marine atmospheres require explicit design validation. Do not assume standard products apply.
5. Neglecting operator training
A VCB is only as reliable as its maintenance regime. Budget for training—improper racking or contact timing adjustment accounts for a measurable share of field failures.
XBRELE manufactures vacuum circuit breakers with vertically integrated production—from CuCr vacuum interrupters through complete breaker assembly. Our 12 kV to 40.5 kV product range serves utility distribution, industrial substations, and renewable energy applications worldwide.
Manufacturing approach: In-house interrupter production with controlled contact metallurgy ensures consistent arc interruption performance and contact longevity.
Certification: IEC type-tested designs with full documentation available for project-specific verification.
Flexibility: OEM and ODM arrangements support panel builders and system integrators requiring customized configurations.
Request technical specifications and type-test certificates for your voltage class and breaking capacity requirements. Our engineering team provides application consultation for altitude derating, environmental sealing, and protection coordination.
Q: How long do vacuum circuit breakers typically last in service?
A: With proper maintenance, VCBs commonly achieve 25–30 years of operational life. The vacuum interrupter component is typically rated for 10,000–30,000 mechanical operations, with actual lifespan depending on switching frequency and fault exposure.
Q: What documentation should I request to verify manufacturer claims?
A: Request the complete IEC 62271-100 or ANSI C37 type-test report—not a summary data sheet. Confirm the tested model and ratings match your specified breaker variant exactly.
Q: How does altitude affect vacuum circuit breaker performance?
A: Above 1,000 m elevation, reduced air density decreases external dielectric strength. Most manufacturers apply derating factors or require enhanced creepage distances for installations above 2,000 m.
Q: What contact material provides optimal switching performance?
A: Copper-chromium alloys containing 25–50% chromium offer the best balance of low contact resistance, arc erosion resistance, and minimal current chopping. Avoid suppliers who do not disclose contact composition.
Q: Should procurement prioritize purchase price or service network proximity?
A: For critical infrastructure, service network proximity typically outweighs initial price advantage. An 8–12 week spare part lead time during an unplanned outage can cost far more than the price differential at purchase.
Q: Can manufacturers outside Europe and North America meet international quality standards?
A: Several Asian manufacturers hold valid IEC type-test certifications from accredited laboratories. Buyers should verify specific product line coverage and consider factory audits for high-value procurements.
Q: How many fault operations should an interrupter withstand?
A: Quality MV vacuum interrupters are rated for 30–50 full short-circuit interruptions at rated breaking capacity. After reaching this threshold, inspection or replacement is recommended regardless of visual condition.