Need Full Specifications?
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
Download our 2025 Product Catalog for detailed drawings and technical parameters of all switchgear components.
Get Catalog
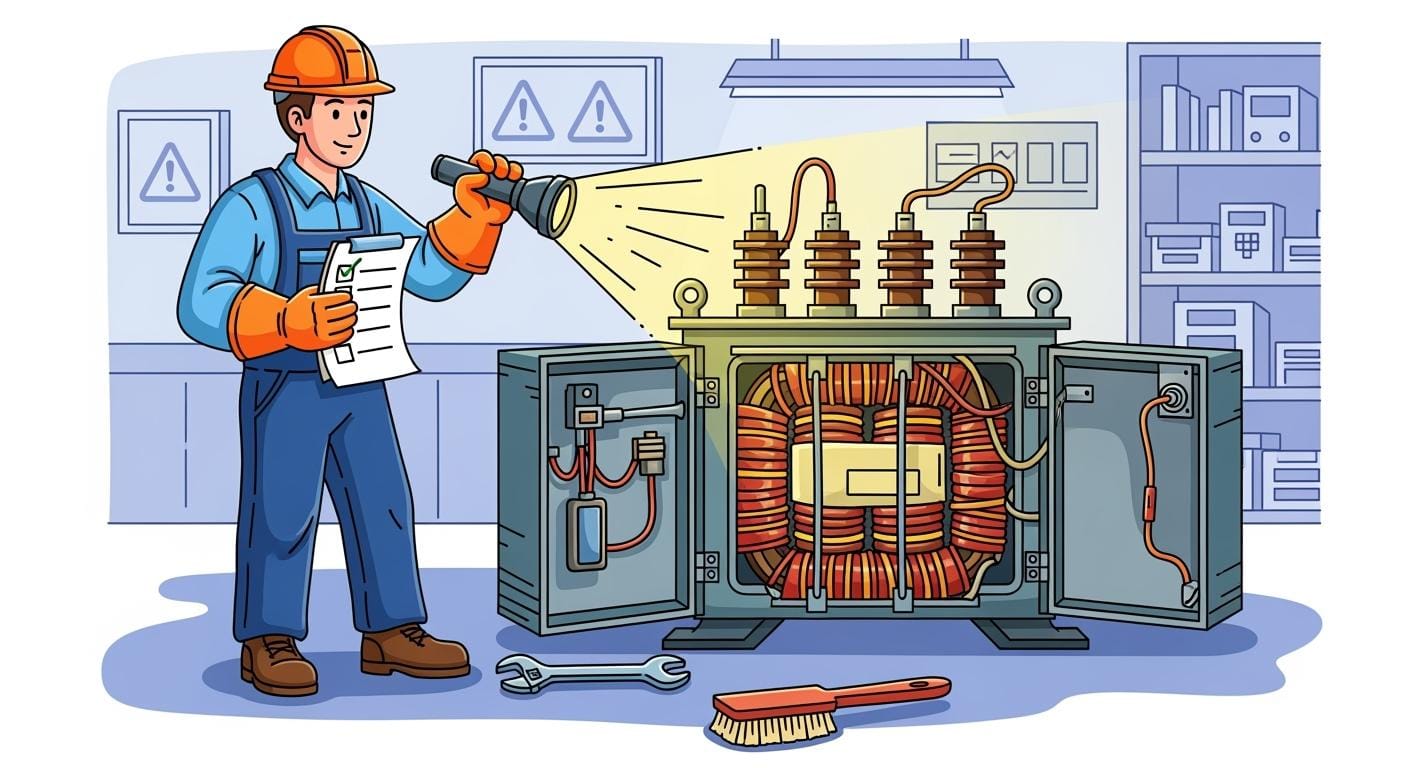
Follow essential dry type transformer maintenance steps to prevent failures, ensure safety, and extend equipment lifespan with regular inspections and cleaning.

You ensure the reliability and longevity of your electrical equipment when you follow a strong dry type transformer maintenance program. Regular inspections and thorough cleaning help prevent costly failures and service interruptions. Schedule quarterly visual checks and comprehensive annual inspections to catch issues early. Neglecting these steps can result in overheating or a shorter transformer lifespan.
Common causes of transformer failure include:
Moisture entering through poor seals or weak joints
Inadequate breather performance
These factors contribute to 90% of transformer failures nationwide
Adopt a proactive, safety-focused approach to protect your operations and avoid unnecessary downtime.
Regular inspections are crucial. Schedule quarterly visual checks and comprehensive annual inspections to catch issues early.
Always wear proper personal protective equipment (PPE) before starting maintenance. This includes insulated gloves, safety glasses, and flame-resistant clothing.
Follow lockout/tagout procedures strictly. Ensure the transformer is de-energized and secured before performing any maintenance tasks.
Maintain a clean work area. Remove debris and ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating and improve safety during maintenance.
Document all maintenance activities. Keep detailed records of inspections, findings, and repairs to track the health of your transformer.
Monitor for signs of overheating and moisture. Address any discoloration, unusual smells, or sounds immediately to prevent failures.
Train your staff regularly. Ensure all personnel understand safety protocols and maintenance procedures to reduce risks and improve efficiency.
Use a preventive maintenance checklist. This helps ensure that all necessary tasks are completed and nothing is overlooked during maintenance.
You must wear the correct personal protective equipment before you begin any dry type transformer maintenance. Select insulated gloves, safety glasses, and flame-resistant clothing for electrical work. Use hard hats and steel-toed boots to protect yourself from falling objects and accidental impacts. Choose hearing protection if you work in noisy environments. Always inspect your PPE for damage or wear before each use. Replace any item that shows signs of deterioration. Proper PPE reduces your risk of electrical shock, burns, and other injuries.
Tip: Keep a checklist of required PPE at the worksite. Review it with your team before starting maintenance tasks.
You must follow strict lockout/tagout procedures to ensure your safety. Shut down the transformer and disconnect it from all power sources. Attach lockout devices to switches and circuit breakers. Place tags on each device to warn others that maintenance is in progress. Verify that the transformer is fully de-energized before you touch any components. Use a voltage tester to confirm zero energy. Only authorized personnel should remove lockout/tagout devices after work is complete.
Lockout/Tagout Steps | Description |
|---|---|
Shut down transformer | Turn off and isolate from all power sources. |
Attach lockout devices | Secure switches and breakers to prevent accidental energization. |
Place warning tags | Inform others that equipment is under maintenance. |
Verify zero energy | Test for absence of voltage before starting work. |
Remove devices after work | Only authorized staff may remove locks and tags. |
You need to prepare the work area to prevent accidents and ensure efficient maintenance. Clear away any debris, tools, or unnecessary equipment from the site. Ensure proper ventilation around the transformer to avoid overheating. Remove obstructions from airflow paths and install filters at ventilation ports to keep dust out. Set up barriers or warning signs to keep unauthorized personnel away from the maintenance zone. Check that lighting is adequate for visibility. Organize your tools and materials so you can access them quickly. Review emergency procedures with your team before you start.
Note: Regular inspections every three to six months in dusty areas and annual checks in clean spaces help maintain a safe environment.
You must follow these safety protocols to protect yourself and your team. The table below summarizes essential safety standards recommended by OSHA and IEC for dry type transformer maintenance:
Safety Protocols | Description |
|---|---|
De-energizing the transformer | Maintenance tasks should only be performed when the transformer is not energized. |
Adequate ventilation | Ensure proper airflow around the transformer and remove any obstructions. |
Regular inspections | Conduct inspections every three to six months in dusty areas; annual checks in clean spaces. |
Cleaning procedures | Use vacuum and dry compressed air to clean components without damaging them. |
Tightening hardware | Regularly tighten accessible hardware to prevent loosening during operation. |
Inspecting for damage | Look for rust, discoloration, or signs of overheating during maintenance checks. |
Installing filters | Use filters at ventilation ports to prevent dust accumulation and maintain airflow. |
Conducting tests | Perform tests to verify the operation of the transformer and identify potential issues. |
You create a safer work environment when you follow these steps. You also reduce the risk of accidents and equipment failure.
You must prepare for emergencies before you start any dry type transformer maintenance. Even with the best safety measures, accidents can happen. A strong emergency plan protects you and your team from serious harm.
Start by identifying possible emergencies. These may include electrical shock, fire, arc flash, or chemical exposure. You should also consider medical emergencies, such as fainting or injury from falling objects. Review your facility’s risk assessment to understand the most likely hazards.
Create a clear emergency response plan. This plan should outline what you and your team must do if an incident occurs. Assign roles to each team member. For example, one person should call emergency services, while another leads the evacuation. Make sure everyone knows their responsibilities.
Post emergency contact numbers in visible locations near the transformer and in the maintenance area. Include numbers for:
Local fire department
Emergency medical services (EMS)
Facility security
On-site safety officer
Tip: Save emergency contacts in your mobile phone and encourage your team to do the same.
You need to establish evacuation routes and assembly points. Mark these routes with clear signs. Practice evacuation drills at least twice a year. These drills help your team respond quickly and calmly during a real emergency.
Keep first aid kits and fire extinguishers close to the work area. Inspect this equipment regularly to ensure it works properly. Train your team to use fire extinguishers and provide basic first aid. You should also know the location of the nearest automated external defibrillator (AED).
Here is a simple emergency planning checklist:
Emergency Planning Task | Frequency | Responsible Person |
|---|---|---|
Review emergency response plan | Annually | Safety Officer |
Update emergency contacts | Quarterly | Facility Manager |
Inspect first aid kits/extinguishers | Monthly | Maintenance Supervisor |
Conduct evacuation drills | Semi-annually | All Staff |
Train staff in first aid/fire safety | Annually | Safety Trainer |
You must report all incidents, even minor ones, to your supervisor. This helps improve future emergency planning and prevents repeat accidents.
Note: A well-practiced emergency plan saves lives and reduces property damage. Do not skip this step in your maintenance routine.
You create a safer workplace when you plan for emergencies. Your preparation ensures that everyone knows what to do if something goes wrong.
You should schedule quarterly visual inspections as part of your dry type transformer maintenance routine. These checks help you catch problems before they become serious. During each inspection, walk around the transformer and look for anything unusual. Use a flashlight to see into dark corners and behind panels. Make sure you document your findings in a maintenance log. This record helps you track changes over time and spot patterns that may indicate developing issues.
Tip: Set reminders for quarterly inspections to ensure you never miss a scheduled check.
You need to pay close attention to signs of wear or damage during every inspection. Early detection prevents costly repairs and unexpected downtime. Look for the following visual indicators:
Rust on clamps and core steel
Carbonization or tracking on windings and insulation
Discoloration of insulation and surfaces, which may signal overheating or loose connections
Frequent inspections allow you to identify these issues before they escalate. You should also check for oil leaks, corrosion, and physical damage to components. If you notice any of these problems, report them immediately and schedule corrective action.
Common Signs of Transformer Wear | What They Indicate |
|---|---|
Rust on clamps/core steel | Moisture ingress, corrosion risk |
Carbonization on windings | Electrical tracking, insulation failure |
Discoloration of insulation | Overheating, loose connections |
Oil leaks | Seal failure, possible contamination |
Physical damage | Mechanical stress, impact |
Note: Regular maintenance helps you detect early signs of wear, overheating, and insulation degradation. Periodic inspections contribute to identifying nascent problems before they escalate.
You must check for dust and dirt buildup during every visual inspection. Dust restricts airflow and causes overheating. Dirt can also attract moisture, which leads to insulation breakdown. Inspect cooling fans, windings, and ventilation ports for any accumulation. Clean these areas using a vacuum or dry compressed air. Remove obstructions from airflow paths to maintain proper cooling.
Dust on windings and fans reduces efficiency
Dirt in ventilation ports increases risk of overheating
Accumulated debris signals poor site housekeeping
You should address dust and dirt promptly to keep your transformer running safely and efficiently. Clean surroundings also make it easier to spot other problems during future inspections.
Alert: In dusty environments, increase inspection frequency to every three months. In cleaner areas, annual checks may be sufficient.
You must inspect the winding surfaces of your dry type transformer during every visual check. The condition of these windings directly affects the performance and safety of your equipment. You should look for discoloration, cracks, and deposits that signal underlying problems.
Start by examining the windings for any change in color. Brown or black marks often indicate overheating. You may see white or chalky residue, which suggests insulation breakdown. Cracks or splits in the winding surface point to mechanical stress or aging. You should also check for foreign materials, such as dust, oil, or moisture. These contaminants can lead to insulation failure and electrical tracking.
Use a flashlight to inspect hard-to-reach areas. Move slowly and observe the entire winding surface. You should pay special attention to corners and edges, where damage often starts. If you notice any unusual odor, such as a burnt smell, investigate further. This may signal overheating or insulation damage.
Tip: Document every observation in your maintenance log. Include photos if possible. This record helps you track changes and plan corrective actions.
You must keep winding surfaces clean and dry. Dust and moisture increase the risk of partial discharge and insulation breakdown. Use a vacuum or dry compressed air to remove loose particles. Avoid using wet cleaning methods, which can introduce moisture.
You should also check for signs of electrical tracking. Look for thin, dark lines running across the winding surface. These lines show that electricity has followed a path outside the intended circuit. Electrical tracking can cause insulation failure and transformer breakdown.
Here is a table summarizing common winding surface issues and their implications:
Winding Surface Issue | What It Means | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
Discoloration (brown/black) | Overheating, loose connections | Investigate source, repair |
Cracks or splits | Mechanical stress, aging | Replace damaged parts |
White/chalky residue | Insulation breakdown | Clean, check insulation |
Dust or debris | Poor airflow, overheating | Clean thoroughly |
Electrical tracking lines | Insulation failure risk | Schedule immediate repair |
Moisture spots | Contamination, corrosion | Dry area, improve sealing |
You must address any issue you find right away. Delaying repairs increases the risk of transformer failure. You should consult your manufacturer’s guidelines for specific cleaning and repair procedures.
Alert: Never ignore winding surface damage. Even minor defects can lead to major failures if left untreated.
You ensure reliable transformer operation when you maintain clean, undamaged windings. Regular inspection and prompt action protect your equipment and extend its lifespan.
You must keep cooling fans clean to ensure proper airflow and prevent overheating. Dust and debris can block the fan blades and reduce cooling efficiency. Start by switching off and de-energizing the transformer. Use a soft brush to loosen dust from the fan blades and grills. Remove the loosened particles with a vacuum cleaner. For stubborn dirt, use a lint-free cloth dampened with a small amount of approved cleaning solution. Avoid spraying liquids directly onto the fans. Always check that the fans spin freely after cleaning. If you notice any unusual noise or vibration, inspect the fan for damage and replace it if necessary.
Tip: Clean cooling fans more often in dusty environments. This practice helps you avoid temperature spikes and extends the life of your transformer.
You need to pay special attention to the windings during dry type transformer maintenance. Dust and dirt on windings can cause insulation breakdown and electrical tracking. Begin by visually inspecting the windings for dust, discoloration, or residue. Use a vacuum cleaner with a soft brush attachment to remove loose particles. For areas that are hard to reach, use dry compressed air in short bursts. Hold the nozzle at a safe distance to avoid damaging the insulation. Never use water or wet cleaning agents on windings. If you find stubborn deposits, consult your manufacturer’s guidelines before using any cleaning chemicals.
Regular cleaning of dust deposited on the bushings of a transformer is essential to avoid flash over across insulators. Frequent flash overs across bushings due to operations in a dusty environment also lead to transformer failures.
You should use a vacuum cleaner or dry compressed air for most cleaning tasks. These methods remove dust without introducing moisture or causing abrasion. Always de-energize the transformer before cleaning. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses and a dust mask. Move the vacuum nozzle slowly over surfaces to capture all debris. When using compressed air, keep the pressure below the manufacturer’s recommended limit to protect insulation and components.
Here is a summary of cleaning methods recommended by transformer manufacturers:
Cleaning Method | Requirement |
|---|---|
Inspection | Regular checks for functionality |
Infrared analysis | Monitoring temperature variations |
Grills cleaning | Requires de-energization of the transformer |
Coil vacuuming | Requires de-energization of the transformer |
You should follow these best practices to keep your transformer clean and reliable. Clean equipment operates more efficiently and lasts longer.
You must remove obstructions from your dry type transformer to maintain safe and efficient operation. Obstructions block airflow, trap heat, and increase the risk of overheating. You should inspect the area around the transformer during every cleaning session. Look for tools, packaging, debris, or misplaced equipment that could restrict ventilation or access.
Start by clearing the floor space around the transformer. Move carts, ladders, and storage bins away from the unit. Sweep up dust, dirt, and small objects. You should check for items that may have fallen behind or under the transformer. Use a flashlight to see into dark corners and tight spaces. Remove any foreign objects you find.
Next, examine the transformer itself. Inspect the cooling fans, grills, and ventilation ports. You may find leaves, paper, or insulation scraps lodged in these areas. Use a vacuum cleaner or dry compressed air to dislodge and remove these materials. Avoid using sharp tools that could damage the equipment.
You should also check for obstructions inside the transformer enclosure. Open access panels only after you have de-energized the unit and followed lockout/tagout procedures. Look for loose wires, cable ties, or mounting hardware that could block airflow or touch live components. Remove these items carefully and store them in a safe location.
Tip: Keep a dedicated storage area for tools and spare parts. This practice prevents clutter and reduces the risk of accidental damage.
You must maintain clear access to all transformer components. Emergency responders need unobstructed paths to reach the transformer in case of fire or electrical fault. You should mark a safety zone around the unit using tape or barriers. Post warning signs to keep unauthorized personnel away.
Here is a checklist to help you remove obstructions effectively:
Task | Frequency | Responsible Person |
|---|---|---|
Clear floor space | Weekly | Maintenance Staff |
Inspect ventilation ports | Monthly | Technician |
Remove debris from fans | Monthly | Technician |
Check inside enclosure | Quarterly | Qualified Electrician |
Mark safety zone | Annually | Facility Manager |
You should document each obstruction you remove in your maintenance log. Record the location, type of obstruction, and any corrective actions taken. This record helps you identify recurring problems and improve housekeeping practices.
Alert: Never ignore obstructions near your transformer. Even small items can block airflow and cause overheating. Prompt removal protects your equipment and ensures reliable performance.
You create a safer and more efficient work environment when you keep the transformer area clear. Regular removal of obstructions supports proper cooling and extends the life of your dry type transformer.
You must approach visual inspection with caution when the transformer remains energized. Only qualified personnel should perform these checks. You need to wear the recommended personal protective equipment and follow all safety protocols. Never touch any exposed components or attempt repairs while the unit is live.
Before you begin, confirm that the area is clear of unnecessary tools and personnel. Stand at a safe distance and use a flashlight to inspect the transformer. Look for signs of overheating, discoloration, or smoke. Check for loose connections, damaged insulation, and any foreign objects near the windings or cooling fans. You should also observe the enclosure for rust, corrosion, or water ingress.
Note: Always restrict maintenance tasks to trained staff. Encourage everyone to follow established safety protocols and create a safety culture in your facility.
You must ensure proper grounding of the transformer to prevent static electricity buildup. If you notice anything unusual, such as sparks or arcing, report it immediately and do not proceed with further inspection.
De-energize and shut down the transformer and its associated circuits if you detect any risk of current leakage.
Confirm that the power is switched off before initiating any maintenance or repair tasks.
You need to monitor the temperature of your dry type transformer during energized operation. Temperature changes can signal developing faults or inefficiencies. Use non-contact infrared thermometers or built-in temperature sensors to check the surface temperature of windings, core, and enclosure.
Record the readings and compare them with manufacturer specifications. If you notice a temperature rise above normal operating limits, investigate the cause. Overheating often results from blocked airflow, excessive dust, or overloaded circuits. You should also check for uneven temperature distribution, which may indicate localized faults.
Tip: Set up automated temperature monitoring systems for continuous tracking. These systems alert you to abnormal conditions and help prevent transformer failure.
Regular temperature monitoring forms a critical part of dry type transformer maintenance. You protect your equipment and extend its lifespan by catching problems early.
Infrared scans offer a powerful, non-invasive way to assess the health of an energized transformer. You use a thermal imaging camera to detect hot spots, abnormal heating, and hidden faults. This method allows you to inspect the transformer without interrupting service or exposing yourself to electrical hazards.
Infrared scanning helps you identify mechanical damage, winding integrity issues, and insulation breakdown. You can benchmark the results for future comparison and monitor changes over time. These scans comply with international standards such as IEC 60076-18 and IEEE C57.149, ensuring reliable diagnostics.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Early Detection of Mechanical Damage | Detects core movement, winding deformation, and other mechanical faults not visible through conventional inspection. |
Assessment of Winding Integrity | Sensitive to winding faults including partial collapse and broken clamping structures. |
Non-Destructive Testing | Completely non-intrusive, allowing safe performance on in-service transformers. |
Benchmark for Future Comparison | Provides a reference point for future condition monitoring of transformer health. |
Compliance with Standards | Follows international standards like IEC 60076-18 and IEEE C57.149 for reliable diagnostics. |
Alert: If you detect any unusual hot spots or temperature anomalies, schedule a comprehensive inspection and corrective action as soon as possible.
Infrared scans should be part of your regular dry type transformer maintenance routine. You gain valuable insights into transformer health and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
You must rely on your senses when performing maintenance on an energized dry type transformer. Unusual sounds or smells often signal early warning signs of internal problems. You can prevent major failures by catching these indicators quickly.
You should listen carefully for any noises that differ from the normal hum of a healthy transformer. Each sound can point to a specific issue:
Buzzing or Humming: A steady, low hum is normal. A loud or irregular buzzing may indicate loose laminations, core vibration, or electrical imbalance.
Crackling or Popping: These sounds often signal arcing, insulation breakdown, or moisture inside the windings.
Clicking or Tapping: Repeated clicks may come from thermal expansion or loose hardware.
Grinding or Squealing: These noises usually mean a problem with cooling fans or bearings.
Tip: Use an electronic stethoscope or a mechanic’s listening rod to pinpoint the source of unusual sounds without touching the equipment.
If you hear any abnormal noise, document the time, duration, and characteristics. You should compare your findings with previous inspection records to spot trends.
You must also use your sense of smell to detect problems. A healthy transformer should not emit strong odors. Pay attention to these warning signs:
Odor Type | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
Burnt or Acrid | Overheating, insulation failure | Investigate immediately |
Chemical or Sweet | Breakdown of varnish or resin | Schedule detailed inspection |
Ozone or Metallic | Electrical arcing | De-energize and inspect for faults |
Musty or Damp | Moisture ingress | Check for leaks and dry the area |
If you notice any of these smells, act quickly. You should never ignore a burnt or chemical odor, as it often means insulation or winding damage.
Stand at a safe distance from the transformer.
Wear appropriate PPE, including a respirator if you expect chemical fumes.
Move slowly around the unit, pausing to listen and sniff at each side.
Record any abnormal findings in your maintenance log.
Report serious issues to your supervisor and schedule further diagnostics.
Alert: Never attempt to open the enclosure or touch components while the transformer is energized. Always follow your facility’s safety protocols.
You improve transformer reliability when you trust your senses and respond quickly to abnormal sounds or smells. Early detection helps you avoid costly repairs and unplanned outages.
You must start internal cleaning only after you have fully de-energized the transformer. This step protects you from electrical hazards and ensures a safe work environment. Begin by opening the transformer enclosure and inspecting all internal components. Use a vacuum cleaner or dry compressed air (set between 20 and 25 psi) to remove dust and dirt from the cooling fans and windings. Focus on areas where debris tends to collect, such as corners and ventilation ports.
You should avoid using water or wet cleaning agents. Moisture can damage insulation and lead to electrical faults. If you find stubborn deposits, gently brush them away with a soft, non-metallic brush. Always wear safety glasses and a dust mask during this process to protect yourself from airborne particles.
Install filters at the bottom ventilation ports to reduce future dust buildup. Replace these filters regularly to maintain proper airflow. Clean equipment operates more efficiently and lasts longer.
Tip: Schedule internal cleaning at least once a year, or more often in dusty environments.
Here is a simple cleaning procedure you can follow:
De-energize the transformer and confirm zero voltage.
Open the enclosure and inspect for dust or debris.
Use a vacuum or compressed air (20–25 psi) to clean fans and windings.
Brush away stubborn dirt with a soft brush.
Install or replace filters at ventilation ports.
You keep your transformer reliable and safe when you follow these steps.
You need to check and tighten all electrical connections during every de-energized maintenance session. Loose connections can cause overheating, arcing, and even transformer failure. Vibration, temperature changes, and aging parts often loosen hardware over time.
Use an insulated torque wrench to tighten accessible bolts, screws, and terminal lugs to the manufacturer’s recommended values. Pay close attention to high-current connections, as these are most prone to loosening. Inspect for signs of discoloration or heat damage, which may indicate a poor connection.
Regularly check all connections to prevent electrical malfunctions.
Tightening connections is crucial for safe and reliable operation.
Record each connection you check and tighten in your maintenance log. This documentation helps you track recurring issues and plan future inspections.
Alert: Never skip this step. Even a single loose connection can lead to costly downtime or equipment damage.
You must inspect tap changers during every dry type transformer maintenance cycle. Tap changers adjust the transformer’s voltage output and play a critical role in stable operation. Over time, contacts inside the tap changer can wear out, corrode, or accumulate carbon deposits.
Start by visually inspecting the tap changer for signs of wear, discoloration, or pitting on the contacts. Use a flashlight to check for dust, dirt, or foreign objects inside the compartment. Clean the area with a vacuum or compressed air if necessary. Do not use solvents or liquids, as these can damage the contacts.
Operate the tap changer through its full range to ensure smooth movement. Listen for any unusual sounds, such as grinding or sticking. If you notice excessive resistance or erratic operation, schedule a detailed inspection or replacement.
Tap Changer Issue | What to Look For | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
Worn contacts | Pitting, discoloration | Clean or replace contacts |
Carbon buildup | Black deposits | Clean with dry methods |
Mechanical problems | Sticking, rough movement | Lubricate or repair |
Loose connections | Visible gaps, arcing marks | Tighten or replace parts |
Note: Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for tap changer maintenance. Improper handling can lead to voltage instability or transformer failure.
You ensure consistent voltage regulation and extend the life of your transformer when you inspect and maintain tap changers properly.
You must check the terminal boards every time you perform de-energized maintenance on your dry type transformer. Terminal boards connect the transformer windings to external circuits. Faults in these areas can cause overheating, arcing, or even transformer failure. Careful inspection helps you prevent electrical faults and ensures reliable operation.
Start by opening the transformer enclosure after confirming zero voltage. Use a flashlight to get a clear view of all terminal boards. Look for loose connections, corrosion, discoloration, or signs of overheating. You should also check for cracked or broken insulators. These issues can lead to short circuits or insulation breakdown.
Follow these steps for a thorough inspection:
Visually inspect all terminals and connections.
Tighten any loose screws or bolts with an insulated tool.
Check for corrosion or rust on metal parts.
Clean dust and debris using a vacuum or dry compressed air.
Examine insulators for cracks, chips, or discoloration.
Look for signs of arcing, such as black marks or melted spots.
Verify that all identification labels are clear and legible.
Tip: Use a maintenance log to record the condition of each terminal board. Include photos if you find any damage.
You should pay special attention to the following warning signs:
Issue Detected | What It Means | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
Loose connections | Risk of overheating/arcing | Tighten immediately |
Corrosion or rust | Poor conductivity, failure | Clean or replace parts |
Cracked insulators | Insulation breakdown risk | Replace insulators |
Discoloration/burns | Overheating, arcing | Investigate and repair |
Dust/debris buildup | Tracking, short circuit risk | Clean thoroughly |
If you find any severe damage, do not re-energize the transformer until you complete repairs. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning and replacing terminal board components.
Alert: Never use water or wet cleaning agents on terminal boards. Moisture can cause insulation failure and electrical hazards.
You improve transformer reliability and safety when you check terminal boards during every maintenance cycle. Consistent inspections help you catch small problems before they become major failures.
You need to watch for overheating during every dry type transformer maintenance session. Overheating is one of the most common and dangerous problems. It can damage insulation, warp windings, and shorten the transformer’s life. You may notice discoloration on the windings, a burnt smell, or even melted insulation. These are clear warning signs.
Common causes of overheating include blocked airflow, overloaded circuits, and loose connections. If you see any of these signs, act quickly. Use temperature sensors or infrared cameras to check for hot spots. Compare your readings with the manufacturer’s recommended limits. If you find temperatures above normal, reduce the load and improve ventilation right away.
Alert: Overheating can lead to unexpected failures and costly downtime. Always address temperature issues as soon as you detect them.
Moisture is a silent enemy for dry type transformers. Even a small amount can cause insulation to break down and fail. You should check for moisture during every inspection. Look for condensation, water stains, or rust on metal parts. Moisture can enter through leaks, poor seals, or during improper storage.
The presence of moisture in insulation can cut its lifespan in half each time the moisture content doubles. Paper insulation absorbs water quickly and decays much faster when wet. Over time, moisture content can increase by 0.1% to 0.2% per year. In old or damaged transformers, moisture levels can exceed 4%, which is very dangerous.
Evidence Description | Impact on Transformers |
|---|---|
Moisture speeds up insulation aging, especially in paper insulation. | Reduces transformer lifespan. |
Moisture causes thermal and chemical breakdown. | Requires lower operating temperatures. |
Moisture content rises over time. | Can reach unsafe levels in old units. |
Higher temperatures with moisture present. | Speeds up insulation aging even more. |
You must keep your transformer dry. Check seals and ventilation regularly. If you find moisture, dry the transformer and fix the source of the leak before returning it to service.
Physical damage can happen during installation, maintenance, or even from outside impacts. You should look for dents, cracks, or broken parts on the transformer body and enclosure. Damaged cooling fans, bent grills, or loose mounting hardware can all affect performance.
Physical damage often leads to other problems, such as poor airflow or exposed windings. You may also see signs of arcing or melted spots near damaged areas. If you find any physical defects, document them and repair or replace the affected parts right away.
Here are some common challenges and solutions you may encounter:
Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
Aging infrastructure | Inspect regularly for wear and tear. |
Overloading and peak demands | Monitor load levels to prevent overloading. |
Insulation deterioration | Test for partial discharge to catch insulation failure early. |
Cooling system failures | Clean and inspect cooling systems often. |
Unexpected failures and downtime | Use smart monitoring for predictive maintenance. |
Tip: Handle transformers with care during transport and installation. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid unnecessary damage.
You protect your equipment and ensure reliable operation when you address these common problems during every dry type transformer maintenance routine.
You must pay close attention to insulation issues during every dry type transformer maintenance session. Insulation keeps electrical currents in their proper paths and prevents dangerous faults. When insulation fails, you risk short circuits, arcing, and even catastrophic transformer failure.
You can spot insulation problems by looking for these warning signs:
Cracks or splits in insulation surfaces
Discoloration, especially brown or black marks
Chalky or powdery residue on windings
Unusual odors, such as burnt or chemical smells
Audible crackling or popping sounds
Alert: Even small cracks or discoloration can signal serious insulation breakdown. Never ignore these signs.
You should use a flashlight to inspect all visible insulation. Pay special attention to corners, edges, and areas near terminals. If you see any damage, document it in your maintenance log and take photos for future reference.
Moisture is a major enemy of insulation. You must keep the transformer dry at all times. Moisture causes insulation to lose strength and break down faster. Check for condensation, water stains, or rust near insulation. If you find moisture, dry the area immediately and fix the source of the leak.
You can use a dielectric absorption test to measure insulation resistance. This test helps you find hidden weaknesses before they cause failures. Compare your results with the manufacturer’s recommended values. If the resistance drops below safe levels, schedule repairs right away.
Here is a table to help you identify common insulation issues and their solutions:
Insulation Problem | What You See or Hear | What You Should Do |
|---|---|---|
Cracks or splits | Visible breaks in insulation | Replace damaged insulation |
Discoloration | Brown or black marks | Investigate overheating |
Chalky residue | Powdery deposits | Clean and check for moisture |
Burnt smell | Acrid or chemical odor | Inspect for overheating |
Low resistance reading | Test result below standard | Schedule immediate repair |
You must avoid using water or wet cleaning agents on insulation. Use only dry methods, such as vacuuming or compressed air. If you need to use cleaning chemicals, always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Tip: Train your maintenance team to recognize insulation issues. Early detection prevents costly repairs and keeps your transformer running safely.
You protect your equipment and your facility when you address insulation problems quickly. Regular inspections and proper cleaning extend the life of your dry type transformer.

Routine testing helps you verify the health and performance of your dry type transformer. You should schedule these tests regularly to catch problems early and maintain reliable operation. Industry standards recommend several routine tests for dry type transformers. The most important ones include insulation resistance, winding resistance, voltage ratio, polarity, no-load losses, short circuit, high voltage, dielectric, applied voltage, induced potential, partial discharge, magnetizing current, power factor, phase relation, and sound level measurement.
You use the turns ratio test to confirm that the transformer windings have the correct ratio. This test checks if the voltage ratio between the primary and secondary windings matches the manufacturer’s specifications. You connect a test set to the transformer terminals and apply a known voltage. The device measures the output voltage and calculates the ratio. If the ratio deviates from the expected value, you may have winding damage or incorrect connections.
Tip: Always record your test results in a maintenance log. Compare them with previous readings to spot trends or sudden changes.
A correct turns ratio ensures that your transformer delivers the right voltage to your equipment. You should perform this test after installation, during routine inspections, and whenever you suspect a problem.
The dielectric absorption test helps you assess the condition of the transformer’s insulation. You apply a DC voltage to the windings and measure the resistance over time. Healthy insulation shows a steady increase in resistance as the voltage remains applied. Low or unstable readings may indicate moisture, contamination, or insulation breakdown.
Test Parameter | What It Reveals | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
High resistance | Good insulation | Continue normal operation |
Low resistance | Moisture or contamination | Dry and clean transformer |
Unstable readings | Insulation breakdown | Schedule repairs |
You should perform this test annually or after any event that could affect insulation, such as water ingress or overheating. Reliable insulation keeps your transformer safe and prevents electrical faults.
You measure winding resistance to detect problems like loose connections, damaged conductors, or shorted turns. You use a digital ohmmeter to check the resistance of each winding. Compare your readings with manufacturer specifications. Significant changes in resistance may signal developing faults.
High resistance often means loose or corroded connections.
Low resistance can indicate shorted turns or damaged windings.
You should test winding resistance during installation, after repairs, and as part of your annual maintenance routine. Document your results and investigate any abnormal values.
Regular winding resistance tests help you prevent overheating and ensure efficient transformer operation.
Routine testing gives you valuable data for predictive maintenance. You can identify issues early and schedule repairs before failures occur. Consistent monitoring supports the reliability and longevity of your electrical assets.
You need to perform a core ground test to ensure the safety and reliability of your dry type transformer. This test checks if the transformer core has a single, solid ground connection. A proper ground prevents dangerous circulating currents and reduces the risk of insulation failure. If you find multiple or floating grounds, you may face overheating, electrical noise, or even catastrophic failure.
To carry out the core ground test, follow these steps:
De-energize the transformer and confirm zero voltage.
Locate the core ground connection, usually found at the base of the core frame.
Use a digital insulation resistance tester (megohmmeter) to measure resistance between the core and earth ground.
Record the resistance value.
A healthy core ground should show a low resistance, typically less than 1 ohm. If you see a high or fluctuating reading, you may have a broken ground strap or loose connection. If you detect more than one ground path, you must correct the wiring immediately.
Tip: Always document your test results in your maintenance log. This record helps you track changes and spot potential problems early.
Here is a quick reference table for interpreting your core ground test results:
Resistance Reading | What It Means | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
< 1 ohm | Proper core grounding | No action needed |
> 1 ohm | Poor or broken ground | Inspect and repair ground |
Fluctuating | Multiple or loose grounds | Correct wiring, retest |
You should perform the core ground test during annual maintenance or after any major repair. This simple check protects your transformer and your facility from electrical hazards.
You must monitor for partial discharge (PD) to maintain the health of your dry type transformer. Partial discharge is a tiny electrical spark that occurs inside insulation when it weakens or degrades. Over time, PD can erode insulation, leading to dangerous faults and transformer failure.
You can detect partial discharge using specialized test equipment. These devices sense high-frequency signals or ultrasonic noise produced by PD activity. You should test for PD during routine inspections, especially if your transformer operates in harsh or humid environments.
Common signs of partial discharge include:
Crackling or hissing sounds near windings
Unusual odors, such as ozone or burning
Visible marks or tracking on insulation surfaces
Alert: Never ignore signs of partial discharge. Even small PD activity can grow quickly and cause major damage.
To perform a partial discharge test, follow these steps:
De-energize the transformer if possible.
Connect the PD detector to the transformer windings or insulation.
Scan all accessible surfaces for PD signals.
Record the location and intensity of any detected activity.
If you find PD, you must investigate the cause. Clean the affected area, improve ventilation, or replace damaged insulation as needed. Always compare your test results with manufacturer guidelines.
Here is a summary of partial discharge warning signs and actions:
PD Indicator | What You Should Do |
|---|---|
Audible crackling | Schedule detailed inspection |
Ozone smell | Check for insulation damage |
Surface tracking | Clean and repair insulation |
You protect your transformer and extend its service life when you test for partial discharge regularly. Early detection helps you avoid costly repairs and unexpected outages.
You need to set up a clear inspection schedule for your transformers. Regular checks help you catch problems early and keep your equipment running smoothly. Most facilities benefit from quarterly visual inspections and a full, detailed inspection once a year. In dusty or high-use environments, you should increase the frequency. Use a calendar or digital reminder system to track upcoming inspections. Assign responsibility to specific team members so nothing gets missed.
Tip: Consistent scheduling reduces the risk of unexpected failures and helps you plan for repairs during low-demand periods.
A sample inspection schedule might look like this:
Inspection Type | Frequency | Responsible Staff |
|---|---|---|
Visual Inspection | Quarterly | Maintenance Tech |
Comprehensive Check | Annually | Senior Technician |
Cleaning | Quarterly | Maintenance Crew |
Testing (e.g., IR, BDV) | Annually | Qualified Engineer |
You should keep detailed records for every maintenance activity. Good documentation helps you spot trends, prove compliance, and plan future work. Record the date, type of inspection, findings, and any repairs made. Include test results, photos, and notes about unusual conditions. Store these records in a central location, either as paper files or in a digital maintenance management system.
Note: Accurate records support warranty claims and make audits easier.
A simple maintenance log entry might include:
Date of inspection
Name of inspector
Checklist of items reviewed
Issues found and actions taken
Test results (e.g., resistance, temperature)
Next scheduled inspection
You can use this information to track the health of your transformer over time and make better decisions about repairs or replacements.
You should always follow the preventive maintenance guidelines provided by your transformer’s manufacturer. These recommendations help you maintain safety and reliability. Most manufacturers suggest the following:
Perform regular inspections and scheduled maintenance to detect issues early.
Monitor for overloading, damaged connectors, and loose plugs.
Follow safety standards such as ISO 9001-2015 or ISO-12000.
Check oil levels and test for breakdown voltage and acidity if your transformer uses oil-filled bushings.
Clean and inspect bushings for cracks and deposits.
Recondition each transformer every 15 to 20 years to improve reliability.
Following manufacturer guidelines ensures your dry type transformer maintenance meets industry standards and keeps your equipment safe.
You should keep a copy of the manufacturer’s manual on hand for reference during every inspection or repair. If you have questions, contact the manufacturer’s technical support for advice.
You need to invest in staff training to maintain the reliability and safety of your dry type transformers. Well-trained personnel can spot problems early, follow correct procedures, and respond quickly to emergencies. You build a strong maintenance program when you give your team the right knowledge and skills.
Start by identifying the essential topics for transformer maintenance training. Your staff should understand:
Safety protocols and PPE requirements
Lockout/tagout procedures
Visual inspection techniques
Cleaning methods for windings and fans
Routine testing procedures
Emergency response steps
You can use a mix of classroom instruction, hands-on practice, and online modules. Practical demonstrations help your team learn how to use tools and test equipment. You should encourage questions and discussions during training sessions. This approach helps everyone understand the material and apply it in real situations.
Tip: Schedule refresher courses every year to keep skills sharp and update your team on new standards or equipment.
You should assign experienced technicians as mentors for new staff. Mentors can share best practices and guide less experienced workers through complex tasks. You build confidence and teamwork when you pair new hires with seasoned professionals.
Consider using a training checklist to track progress and ensure all staff meet your facility’s standards. Here is an example:
Training Topic | Completed | Date | Trainer |
|---|---|---|---|
Safety protocols | ☐ | ||
Lockout/tagout procedures | ☐ | ||
Visual inspection techniques | ☐ | ||
Cleaning procedures | ☐ | ||
Routine testing | ☐ | ||
Emergency response | ☐ |
You should keep records of all completed training sessions. These records help you prove compliance during audits and identify areas for improvement.
You need to stay updated on industry standards and manufacturer recommendations. Encourage your team to attend workshops, webinars, or certification programs. You can also invite experts to lead specialized training sessions on new equipment or advanced testing methods.
Alert: Never allow untrained staff to perform transformer maintenance. You reduce the risk of accidents and equipment damage when you ensure everyone is properly trained.
You create a safer and more efficient workplace when you prioritize staff training. Your team will work confidently, follow procedures, and help extend the life of your dry type transformers.
You strengthen your facility’s reliability when you follow dry type transformer maintenance best practices.
Schedule regular inspections and cleaning to prevent dust buildup and overheating.
Perform maintenance only when the transformer is de-energized for safety.
Tighten hardware and replace loose insulation to avoid operational issues.
Install filters at ventilation ports to improve airflow.
Check for overheating or loose connections during every inspection.
Neglecting preventive maintenance can result in poor performance, transformer failure, and hazardous situations. Always use a preventive checklist and consult experts for complex repairs. Start your maintenance program today to protect your assets and ensure safe operation.
You should perform visual inspections every quarter and schedule comprehensive maintenance annually. In dusty or harsh environments, increase inspection frequency to every three months. Always follow your manufacturer’s guidelines for specific intervals.
You should never clean internal components while the transformer is energized. Only perform non-invasive visual inspections and temperature checks with proper PPE. Always de-energize the unit before any cleaning or hands-on maintenance.
Look for overheating, discoloration, unusual noises, burnt smells, and visible damage. Moisture, dust buildup, and loose connections also signal trouble. Early detection helps you prevent costly failures.
Partial discharge testing helps you detect insulation breakdown before it leads to major faults. Early identification of PD activity allows you to schedule repairs and avoid unexpected transformer outages.
Install filters at ventilation ports and maintain a clean environment around the transformer. Schedule regular cleaning and inspections. Remove obstructions and debris promptly to ensure proper airflow.
You must dry the transformer immediately and locate the source of the leak. Repair seals or ventilation issues before returning the unit to service. Moisture can quickly degrade insulation and cause failures.
Only qualified and trained personnel should perform transformer maintenance. You reduce risks and ensure compliance with safety standards when you use experienced technicians.
Maintain a log with inspection dates, findings, test results, repairs, and photos. Good records help you track equipment health, plan future maintenance, and support warranty claims.